The term “sight glass” refers to the transparent glass tube or window component of an industrial or commercial piece of equipment that allows observers to have a clear view of what is occurring within the container.
While sight glasses can serve a wide range of functions, they are primarily used for visibility. They allow operators to visually monitor the processes that occur within tanks, pipes, and other enclosed pieces of equipment. Many tanks and boiler systems contain sight glasses to help guarantee optimal quality and prevent the development of hazardous operational conditions.
Applications
Sight glasses find application in a broad spectrum of industries, such as:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Biofuels
- Food and beverage processing
- Utilities and energy
- Chemical/petrochemical
- Wastewater treatment and management
Within these industries, they are used in a variety of equipment and systems, including:
- Fluid handling systems
- Boiler systems
- Industrial burners
- Pulp and paper processors
- Oil and gas refineries
- Automobiles and other transport vehicles
- Combustion equipment
There are two different types of sight glasses available for use in industrial and commercial equipment and systems: sight glass windows or sight port windows.
 Sight glass windows are comprised of transparent glass materials fused to metal frames that function as single-piece components. Some of the advantages of this type of design are that the glass strengthens as it experiences compressive forces (rather than tension), and the metal frame absorbs the bulk of the mounting stress. This latter quality allows the window to withstand general wear and tear, residue, and uneven bolts. Manufacturers generally consider sight glass windows to be highly cost-effective and reusable.
Sight glass windows are comprised of transparent glass materials fused to metal frames that function as single-piece components. Some of the advantages of this type of design are that the glass strengthens as it experiences compressive forces (rather than tension), and the metal frame absorbs the bulk of the mounting stress. This latter quality allows the window to withstand general wear and tear, residue, and uneven bolts. Manufacturers generally consider sight glass windows to be highly cost-effective and reusable.
Sight glass that is installed on tanks with a lighting component is referred to as a sight port window or a viewport. Sometimes there are two sight glasses mounted onto a tank: one on the top that allows exterior light to shine into the tank compartment, and another on the side that allows the operator to view the illuminated interior of the tank.
Material Selection
There are several key factors to keep in mind when determining and selecting the appropriate source material to use for a sight glass. These factors include:
Maximum expected temperature
Operational temperatures within the equipment or system can affect the performance of the sight glass materials. Some materials are only suitable for operating temperatures less than 300°F, while others are effective above 500°F.
Thermal shock
Sight glass engineers must take rapid temperature change into consideration. Glasses that have high thermal expansion coefficients, low thermal conductivity, and low durability are not suitable for working environments that feature rapid or extreme fluctuations in temperature. Engineers use the following formula to determine the resistance of a particular material to thermal shock (also referred to as the Thermal Shock Parameter):
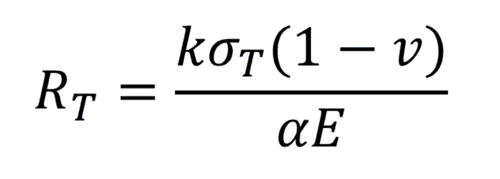
In this equation, k is thermal conductivity, σT is the maximum tension the material can withstand, α is the thermal expansion coefficient, E is the Young’s modulus, and ν is the Poisson ratio.
Corrosion
Certain caustic or acidic substances can cause the sight glass to become “cloudy” which hinders interior visibility and compromises the overall integrity of the glass window. In applications that are subjected to such conditions, glass material with high corrosion resistance should be used.
Abrasion
Rough particles or other abrasive elements can gradually erode the sight glass, obstructing the operator’s view and reducing the structural integrity of the component. Designers should use thick and durable materials in abrasive environments. Regular inspections are also essential to maintaining the longevity of sight glasses.
Pressure
In regard to sight glasses, pressure can refer to the working, design, test, or burst pressure. Once all of these values are determined, it is important to select a material (and a material thickness) that is capable of achieving them.
Impact
Some applications experience objects occasionally impacting against the sight glass (e.g., in food processors where matter is thrown against the glass, or workers accidentally dropping a tool on the surface of the viewport). To reduce the chance of component failure, engineers should select durable materials for their sight glasses, such as fused sight glasses.
Sight glasses are available in a wide range of materials with a variety of chemical properties. While some of these applications can employ plastic sight glasses, generally the environmental and operational conditions these components experience (such as extreme temperatures, pressure, exposure to caustic or abrasive elements, or thermal shock) call for a more durable and effective material—i.e., glass.
Some of the glass materials used to construct sight glasses include:
- Fused silica: Fused silica, such as Corning’s Blue Vycor®, boasts a unique cross-linked three-dimensional structure that demonstrates excellent resistance to thermal shock, near-zero thermal expansion, and UV transparency. It is optimal for high temperature environments and rapid temperature changes.
- Industrial fused silica: Industrial fused silica is an enhanced, commercial-grade version of fused silica that many companies use for heavy duty sight glass applications.
- UV fused silica:This material is well-suited for applications that require a low content of inclusions, and/or a high refractive index homogeneity for superior visual accuracy.
- Soda lime: Soda lime silica glass is commonly used in window panes and glass containers. While this material generally has poor resistance to thermal shock, corrosion, and abrasion, it can be re-softened and re-melted for reuse in multiple applications. Companies in the food and beverage industry often utilize this material.
- Laminated soda lime: Laminated glass is formed by inserting an interlayer between two or more pieces of glass. The interlayer, once broken, binds the adjacent glass together and increases its strength. Laminated glass is frequently utilized in architectural, automotive, and bulletproofing applications.
- Float glass: Float glass, such as Schott®’s Borofloat® Glass, is suitable for optical applications that require high transparency and visibility, such as windows and display glasses. It is also a very good glass to use when dealing with fluctuating temperatures. It has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. Schott® Borofloat® Glass provides uniform thickness and an extremely flat surface for optimal viewing.
- Borosilicate: Due to its affordability, borosilicate is very popular among a diverse set of industries, such as the biomedical and research industries. Borosilicate boasts above-average thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, and abrasion resistance, as well as exceptional toughness and durability under constant pressure and sudden impact conditions. It also remains highly transparent when exposed to high temperatures.
Sight Glasses by Swift Glass
Sight glasses are used throughout industry to facilitate optimal performance and safe operation of equipment and systems. The importance of these components necessitates careful consideration during the design and construction phases, especially in regard to the glass construction materials.
Swift Glass is an ISO 9001:2015 certified and ITAR registered privately owned global company that specializes in the fabrication of high quality glass parts. For nearly a century, we have satisfied customers in need of custom fabricated glass components with our exceptional service, top-tier products, and a reliable support network. Our expertise and experience allow us to fabricate superior sight glass components tailored to your unique needs.
We provide sight glass from the following brands:
- Schott®
- Corning®
- Pilkington
- Optivex™
- MAXOS®
To learn more about the advantages of working with us for your next project, be sure to contact our team to request a quote today.